chemical vapor deposition
Chemical vapor deposition is a chemical technology that mainly uses one or several gas phase compounds or elements containing thin film elements to react chemically on the surface of a substrate to form a thin film. Chemical vapor deposition is a new technology developed in recent decades for the preparation of inorganic materials. Chemical vapor deposition has been widely used to purify substances, develop new crystals, and deposit various single crystal, polycrystalline or glassy inorganic thin film materials. These materials can be oxides, sulfides, nitrides, carbides, or binary or multi-element interelement compounds in groups III-V, II-IV, IV-VI, and their physical functions can be passed through the gas phase. The doped deposition process is precisely controlled. At present, chemical vapor deposition has become a new field of inorganic synthetic chemistry.

application
Modern science and technology require the use of a large number of new inorganic materials with different functions. These functional materials must be highly pure, or doped materials formed by intentionally doping certain impurities into high-purity materials. However, many of the preparation methods we are familiar with in the past, such as high-temperature smelting, precipitation and crystallization in aqueous solutions, are often difficult to meet these requirements and cannot guarantee high-purity products. Therefore, the synthesis of new inorganic materials has become a major topic in modern materials science. [1]
principle
Chemical vapor deposition technology is a process that uses gaseous substances to produce chemical reactions and transport reactions on solids to produce solid deposits. It roughly consists of three steps:
(1) Formation of volatile substances;
(2) Transfer of the above substances to Deposition area;
(3) Produce chemical reactions on solids and produce solid matter.
The most basic chemical vapor deposition reactions include thermal decomposition reactions, chemical synthesis reactions, and chemical transport reactions.
Features
1) At medium or high temperatures, solid substances are deposited on the substrate to form solid substances through gas-phase chemical reactions between gaseous initial compounds.
2) It can be deposited under normal pressure or vacuum conditions (negative pressure ", usually vacuum deposition film quality is better).
3) The use of plasma and laser-assisted technology can significantly promote chemical reactions, allowing deposition at lower temperatures 4
) The chemical composition of the coating can change with the change of the gas phase composition, so as to obtain a gradient deposit or a mixed coating. 5
) The density of the coating and the purity of the coating can be controlled.
Coating on complex-shaped substrates and granular materials. It is suitable for coating various complex-shaped workpieces. Due to its good wrapping performance, it can coat workpieces with grooves, grooves, holes, and even blind holes.
7 ) The deposited layer usually has a columnar crystal structure and is not resistant to bending, but chemical reactions can be perturbed in the gas phase through various techniques to improve its structure.
8) A variety of metal, alloy, ceramic and compound coatings can be formed through various reactions . . [2]
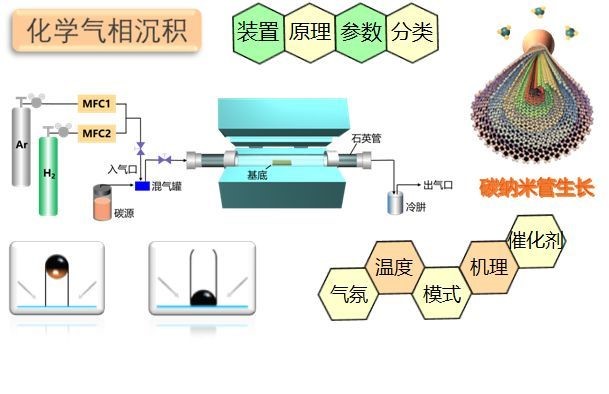
technology type
The most important component of the chemical vapor deposition device is the reactor. According to the difference in reactor structure, we can divide chemical vapor deposition technology into two types: open tube/sealed tube gas flow method:
1. The sealed tube method
is a reaction method that places a certain amount of reacting substances and collectives on both sides of the reactor. , evacuate the reactor, then inject part of the transport gas into it, and then seal it again, and then control the temperature at both ends of the reactor to make it have a certain difference. Its advantages are: ① It can effectively avoid external pollution; ② No need Continuous pumping can keep the vacuum inside. Its disadvantages are: ① The material production speed is slow; ② The pressure in the tube is not easy to control.
2 Open tube method
The characteristic of this preparation method is that the reaction gas mixture can be replenished at any time. The exhaust gas can also be discharged from the reaction device in time. Based on the heating method, the open-tube airflow method should be divided into two types: hot wall and cold wall. The heating of the former will heat up the entire deposition chamber wall, so deposition will also occur on the tube wall. In the latter, only the body itself will be heated, so it does not have the above shortcomings. Cold wall heating generally uses induction heating, electric heating, infrared heating, etc. [1]
Chemical vapor deposition technology used in material preparation
1 Chemical vapor deposition method to produce crystals and crystal thin films.
The chemical vapor deposition method can not only help improve the properties of crystals or crystal thin films, but can also produce many crystals that cannot be prepared by other means. The most common way chemical vapor deposition is used is to generate a new epitaxial single crystal layer on a certain crystal substrate. It was first used to prepare silicon, and later it was used to prepare epitaxial compound semiconductor layers. It is also common in the preparation of metal single crystal films (such as the preparation of W, Mo, Pt, Ir, etc.) and individual compound single crystal films (such as nickel ferrite films, yttrium iron garnet films, cobalt ferrite films, etc. ).
2 Production of Whiskers
Whiskers are a kind of single crystal that is thought to grow. It plays a great role in the field of composite materials and can be used to produce some new composite materials. Chemical vapor deposition uses the hydrogen-reducing properties of metal halides when producing whiskers. The chemical vapor deposition method can not only prepare various metal whiskers, but also produce compound whiskers, such as alumina, emery, titanium carbide whiskers, etc.
3. Chemical vapor deposition technology to produce polycrystalline/amorphous material films.
Chemical vapor deposition method is widely used in the semiconductor industry. For example, a polysilicon deposition layer as an edge dielectric isolation layer. In contemporary times, new amorphous materials are increasingly used in microelectronic components. Such materials include phosphosilicate glass, borosilicate glass, SiO2, Si3N4, etc. In addition, there are also some materials that may be developed into switches and storage memory materials in the future, such as copper oxide-phosphorus pentoxide, copper oxide-vanadium pentoxide-phosphorus pentoxide, and vanadium pentoxide-phosphorus pentoxide, etc. Produced using chemical vapor deposition. [1]
Use of chemical vapor deposition method in precious metal materials
1 Several precious metal films are produced by chemical vapor deposition.
Precious metal films have attracted the interest of researchers because of their good anti-oxidation ability, high conductivity, strong catalytic activity and extreme stability. Compared with other methods of producing precious metal films, the chemical vapor deposition method has more technical advantages, so most precious metal films are prepared using this method. There are a wide range of deposition materials used to deposit precious metal films, but most of them are halides and organic compounds of precious metal elements, such as COCl2, platinum carbonyl chloride, iridium carbonyl chloride, DCPD compounds, etc.
2 Chemical vapor deposition method to produce noble metal iridium high-temperature coating.
Starting in the 1980s, NASA began to try to use metal organic compound chemical vapor deposition method to produce composite nozzles using rhenium-based iridium as coating, and achieved success. At this time, chemistry The vapor deposition method has made a certain breakthrough in the field of producing precious metal coatings.
NASA used C15H21IrO6 as the material to make the iridium coating, and used the thermal decomposition reaction of C15H21IrO6 for deposition. The deposition speed of iridium is very fast, which can reach 3~20μm/h. The deposition thickness has also reached 50μm, and the production efficiency of C15H21IrO6 is as high as more than 70%.
3 Palladium chemical vapor deposition
Pd and its alloys have extremely strong adsorption of hydrogen and special selective permeability properties, and are an ideal material for storing or purifying hydrogen. Most of the current uses of Pd are palladium alloys or palladium coatings to produce hydrogen purification equipment. Some scholars also use chemical vapor deposition to form palladium into films or thin layers. The specific method is to use metal organic compounds with extremely low decomposition temperatures as materials for preparing palladium, including: allyl [β-ketimine] Pd (Ⅱ), Pd (η-C3H5) (η-C5H5) and Pd ( Materials such as eta-C3H5) (CF3COCHCOCF3) can be used to produce very pure palladium films using this method.
Chemical vapor deposition technology is an important material preparation method and plays an important role in precious metal films and coatings. Currently, my country is still in the development stage in the aerospace field, and the use of chemical vapor deposition technology still has a lot to explore. Space requires us to invest more energy in research.